Konungariket Sverige
(Kingdom of Sweden)
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden has not participated in any war in almost two centuries. An armed neutrality was preserved in both World Wars. Indecision over the country's role in the political and economic integration of Europe caused Sweden not to join the EU until 1995, and to forgo the introduction of the euro in 1999.
Ruled by King Carl XVI Gustaf (since 19 September 1973); Heir Apparent Princess Victoria Ingrid Alice Desiree, daughter of the monarch (born 14 July 1977). Prime Minister is Goran Persson (since 21 March 1996).
Capital of Sweden is Stockholm, and Flag Day, 6 June (1523, Gustav VASA elected king) is the National holiday.
|
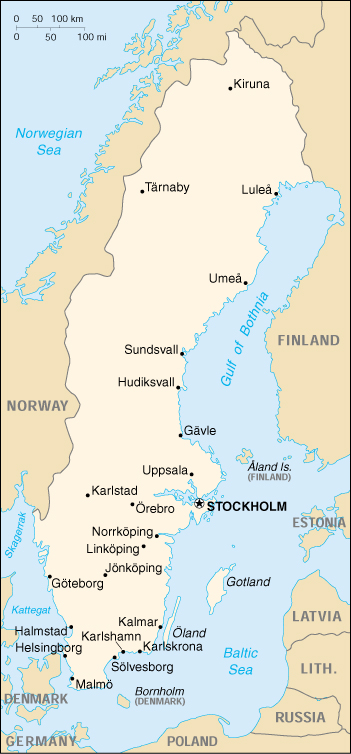
Location: Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway.
The area is approximately 449,964 sq km (410,934 sq km land. 39,030 sq km water). Terrain is mostly flat to gently rolling lowlands. Mountains in west. Natural hazards are the ice floes in the surrounding waters, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia, which can interfere with maritime traffic. Climate is temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers. Subarctic in north.
Population: About 8,878,085 people live in Sweden.
An indigenous population: Swedes and Finnish and Sami minorities. Ethnic groups also include foreign-born or first-generation immigrants: Finns, Yugoslavs, Danes, Norwegians, Greeks, Turks. Main language spoken is Swedish. Also, small Lapp- and Finnish-speaking minorities.
Religious Denomination: Lutheran (87%), Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish, and Buddhist.
Agriculture: Products include grains, sugar beets, potatoes, meat, and milk.
Economy: Aided by peace and neutrality for the whole twentieth century, Sweden has achieved an enviable standard of living under a mixed system of high-tech capitalism and extensive welfare benefits. It has a modern distribution system, excellent internal and external communications, and a skilled labor force. Timber, hydropower, and iron ore constitute the resource base of an economy heavily oriented toward foreign trade. In recent years, however, this extraordinarily favorable picture has been somewhat clouded by budgetary difficulties, high unemployment, and a gradual loss of competitiveness in international markets. Sweden has harmonized its economic policies with those of the EU, which it joined at the start of 1995.
Currency: Swedish krona (SEK).